
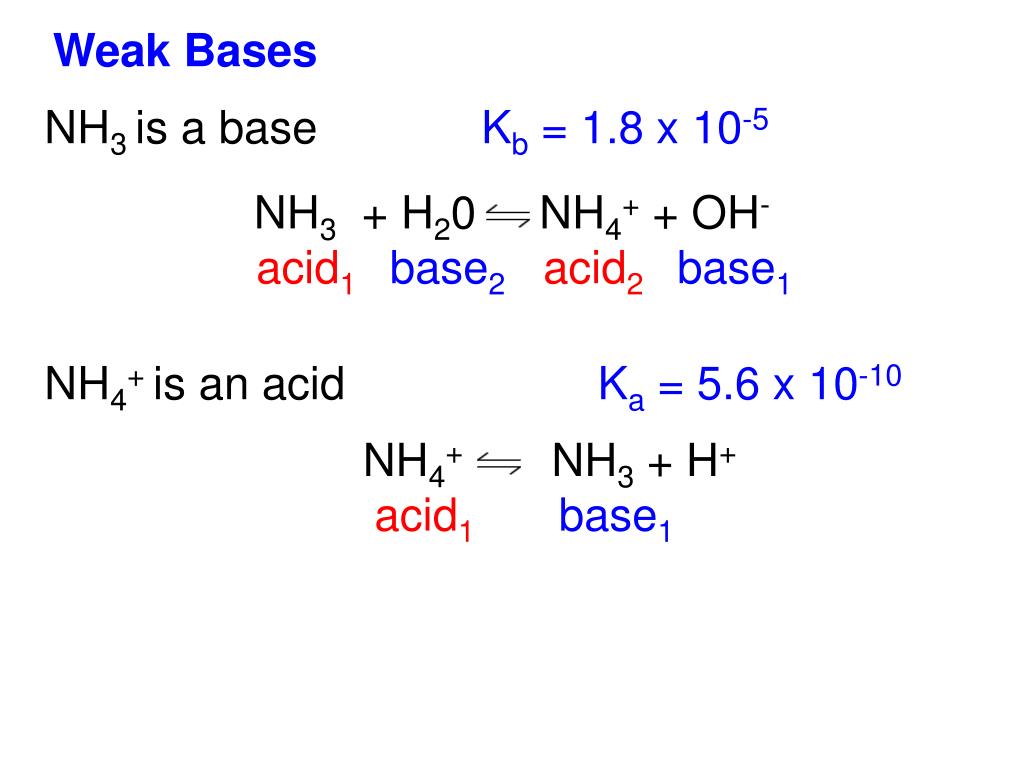

The three dipoles pointing in the same direction provide a net dipole moment, which creates polarity.įurthermore, the lone pair on the nitrogen atom exerts an outward strain on the bond, causing the structure of NH3 to become asymmetrical. This acid-base chart includes the K a value for reference along with the chemicals formula and the acid’s conjugate base. The three N-H bonds produce three dipole moments in one direction due to the variation in their electronegativities. The N–H bond is polar because of the electronegativity difference between N (3.04) and H (2.2). The uneven distribution of charges among nitrogen and hydrogen atoms causes polarity. In each bond, nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen. NH3 is polar because it has three N-H bond dipoles that do not cancel out. Conjugate acid is formed when an acid donates a proton to a base. A conjugate acid contains one more H atom and one more + charge than the base that formed it. The chloride ion is the conjugate base of. Ammonia ( N H3 ) is a base because is 'accepts H+ from water to come its conjugate acid, the ammonium ion ( N H+ 4 ). Since ammonia is a weak base, Kb is measurable and Ka > 0 (ammonium ion is a weak acid). NH 4 + ( a q) + H 2 O ( l) H 3 O + ( a q) + NH 3 ( a q) K a K w / K b. Molar mass of Ammonia (NH3)= 14.0067 g/mol + (3× 1.00794) g/mol = 17.03052 g/mol As we see the acid and base concept, so according to lewis theory of acid and base, any compound is an acid if it accepts or. The ammonium ion is the conjugate acid of the base ammonia, NH 3 its acid ionization (or acid hydrolysis) reaction is represented by. The molecular mass of nitrogen is 14.0067 g/mol.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
